This project involved a comprehensive analysis of global cyberattack data spanning from 2015 to 2024, focusing on identifying patterns, trends, and impacts across various industries and geographic regions. By leveraging data science techniques, I was able to extract valuable insights about the nature of cyber threats, their evolution over time, and their financial implications for businesses worldwide.

The dataset contained detailed information about thousands of cyberattack incidents, including attack types, attack sources, defense mechanism, security vulnerability, target industries, geographic locations, estimated financial losses and number of impacted users. Through careful analysis and visualization, I was able to identify critical trends that could help organizations better prepare for and respond to cyber threats in an increasingly digital business environment.
This analysis was motivated by the rapid increase in both frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks worldwide, and the growing economic impact these attacks have on organizations of all sizes. By understanding the patterns and correlations in historical attack data, security professionals can better allocate resources and develop more effective defensive strategies.
The analysis was conducted using Python with libraries including Pandas for data manipulation, Seaborn and Matplotlib for visualization, and NumPy for statistical calculations. The methodology included:
Visualizations played a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of cyberattacks and communicating findings. The project produced several insightful visualizations that revealed patterns in cybersecurity threats.
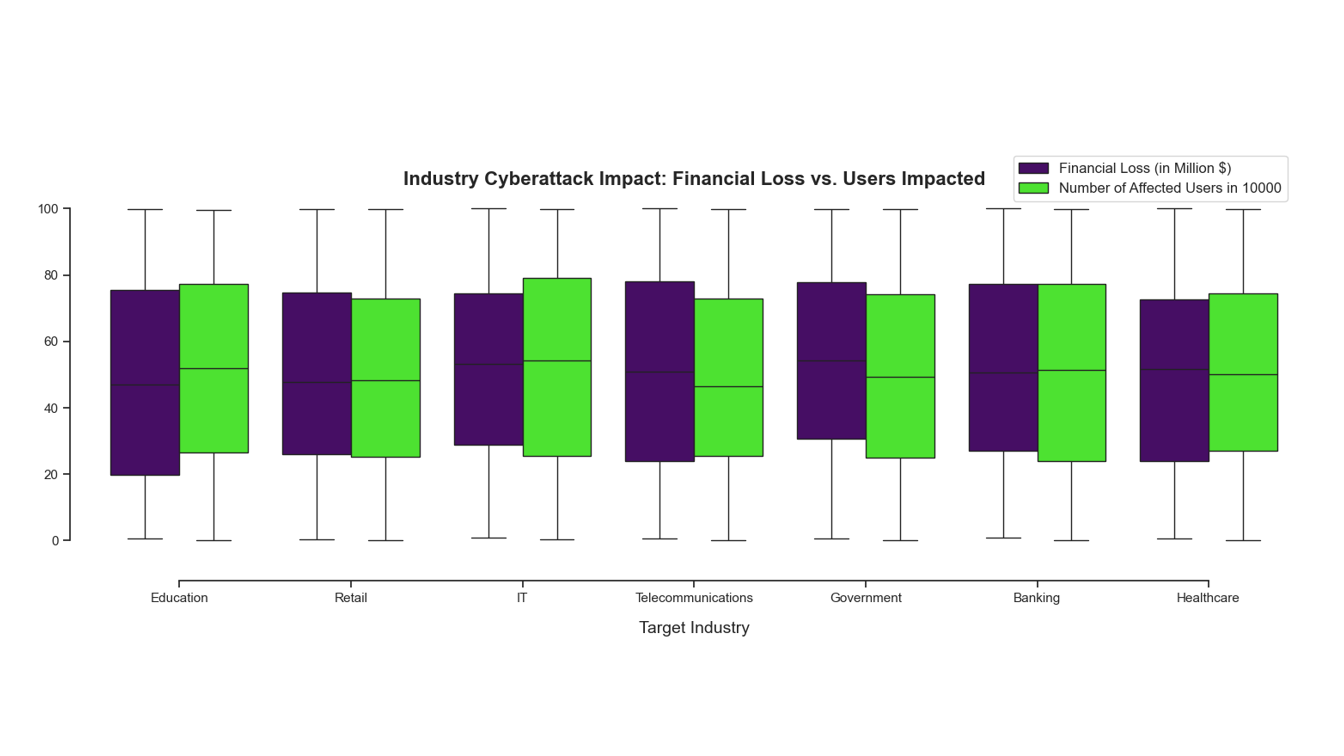
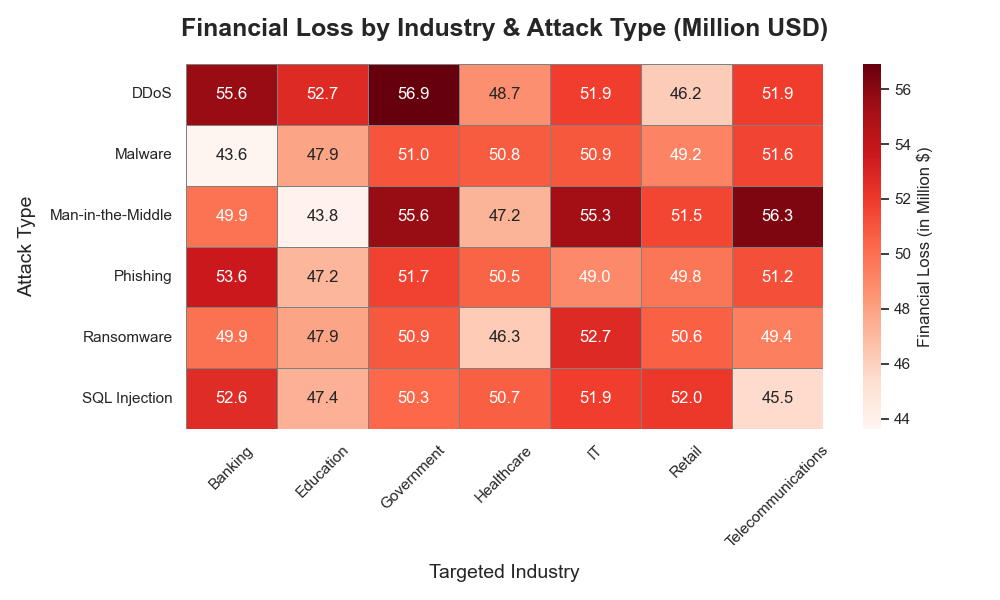
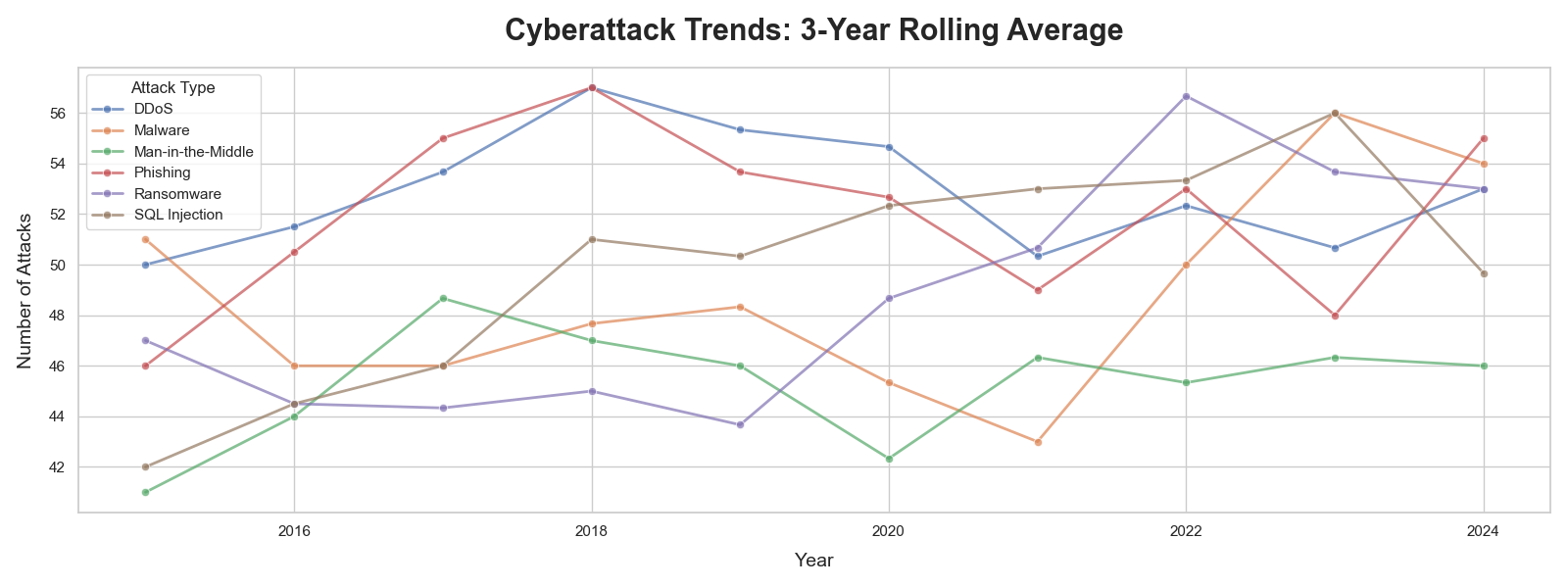
The analysis revealed several key insights into global cybersecurity threats during the 2015-2019 period:
This analysis highlights the growing sophistication and their financial impact of cyberattacks across global industries. The findings suggest that organizations need to implement adaptive security strategies that address the evolving nature of cyber threats, particularly in vulnerable sectors. Future work could expand this analysis to include more recent data and explore the impact of emerging attack vectors like AI-powered threats and supply chain vulnerabilities.